|
Cloxacillin
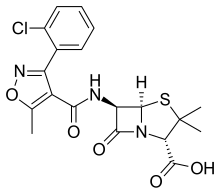
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of several bacterial infections.[1] This includes impetigo, cellulitis, pneumonia, septic arthritis, and otitis externa.[1] It is not effective for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).[2] It can be used by mouth and by injection.[1] Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis.[1] Clostridioides difficile diarrhea may also occur.[2] It is not recommended in people who have previously had a penicillin allergy.[1] Use during pregnancy appears to be relatively safe.[1] Cloxacillin is in the penicillin family of medications.[2] Cloxacillin was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1965.[3] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[4] It is not commercially available in the United States.[2] Mechanism of actionIt is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin. Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, which does not allow the beta-lactamases to bind. This drug has a weaker antibacterial activity than benzylpenicillin, and is devoid of serious toxicity except for allergic reactions.[citation needed] Society and cultureCloxacillin was discovered and developed by Beecham (now GlaxoSmithKline).[5] It is sold under a number of trade names, including Cloxapen, Cloxacap, Tegopen and Orbenin.[6] See alsoReferences
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||