|
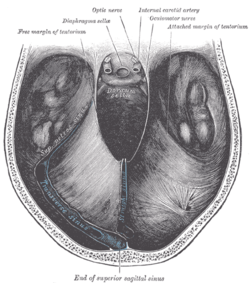
Diaphragma sellae
The diaphragma sellae or sellar diaphragm is a small, circular sheet of dura mater forming an (incomplete) roof over the sella turcica and covering the pituitary gland lodged therein. The diaphragma sellae forms a central opening to accommodate the passage of the pituitary stalk (infundibulum)[1] which interconnects the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. The diaphragma sellae is an important neurosurgical landmark.[1] AnatomyBoundariesThe diaphragma sellae has a posterior boundary at the dorsum sellae and an anterior boundary at the tuberculum sellae along with the two small eminences (one on either side) called the middle clinoid processes. VariationThe opening formed by the diaphragma sellae varies greatly in size between individuals.[1] Clinical significancePituitary tumours may grow to extend superiorly beyond the diaphragma sellae.[1] Violation of the diaphragma sellae during an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary tumor resection will result in a cerebrospinal fluid leak.[citation needed] Additional images
References
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||