Districts of Japan
|
Read other articles:

EurodanceOrigini stilisticheDanceHouse[1] Euro disco[2] hi-NRG[1] techno[2] trance dance pop hip house Hip hop [2] New beat Origini culturaliFine anni ottanta in Belgio, Paesi Bassi e Germania.[3] Strumenti tipicisintetizzatore, drum machine, tastiera, sequencer PopolaritàAnni novanta SottogeneriEuro house - Euro techno - Euro hop - Italodance - Bubblegum dance Generi correlatiHard dance, Euro reggae Categorie correlateGruppi musicali eurodance &#…

Joaquín SabinaInformasi latar belakangNama lahirJoaquín Ramón Martínez SabinaLahir12 Februari 1949 (umur 75)AsalÚbeda, Jaén, SpainGenreLatin, rock, trovaPekerjaansinger-songwriterTahun aktif1978–presentLabelBMG Ariola SpainSitus webJSabina.com Joaquín Sabina (lahir 12 Februari 1949) adalah seorang penyanyi berkebangsaan Spanyol. Pengawasan otoritas Umum Integrated Authority File (Jerman) ISNI 1 VIAF 1 WorldCat Perpustakaan nasional Norwegia Spanyol Prancis (data) Catalunya The ICCU…

Massacres of Poles by Ukrainian nationalists during World War II Massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern GaliciaPart of the Eastern Front of World War IIPolish victims of a massacre committed by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army in the village of Lipniki, Wołyń (Volhynia), 1943LocationVolhyniaEastern GaliciaPolesieLublin regionDate1943–1945TargetPolesAttack typeMassacre, ethnic cleansing, considered a genocide in PolandDeaths120,000 Poles[1] 340 Czechs[2]PerpetratorsOrganizatio…

Federasi Sepak Bola VanuatuOFCDidirikan1934Kantor pusatPort VilaBergabung dengan FIFA1988Bergabung dengan OFC1988PresidenLambert MaltockWebsitewww.vanuafoot.vu Federasi Sepak Bola Vanuatu adalah badan pengendali sepak bola di Vanuatu. Kompetisi Badan ini menyelenggarakan beberapa kompetisi di Vanuatu, yakni: Liga Divisi Utama Vanuatu Liga Divisi Dua Vanuatu Tim nasional Badan ini juga merupakan badan pengendali dari satu – satunya tim nasional di Vanuatu, yakni tim nasional senior pria Vanuatu…

(Selengkapnya) Terlepas isinya sebelum dialihkan, halaman bahasa Musi dan rumpun bahasa Musi merupakan topik yang valid dan dapat dibedakan dari bahasa Palembang. Berdasarkan survei komprehensif ragam-ragam Melayik Sumbagsel oleh McDowell & Anderbeck (2020), penggolongannya kurang lebih seperti ini: Melayik Musi (= rumpun bahasa Musi = [mui] + [liw] = musi1243) Musi Hulu Musi (= bahasa Musi = [mui] sebelum merger dg kode lain = nucl1812) Sekayu Kelingi Penukal Palembang-Dataran Rendah Palemb…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Hokkaïdo (homonymie). Hokkaidō北海道 (ja) Carte de Hokkaidō. Géographie Pays Japon Archipel Archipel japonais Localisation Mer du Japon, mer d'Okhotsk et océan Pacifique Coordonnées 43° N, 142° E Superficie 83 456,64 km2 Point culminant Asahidake (2 291 m) Géologie Île continentale Administration Préfecture Hokkaidō Démographie Population 5 231 685 hab. (30 novembre 2020) Densité 62,69&…
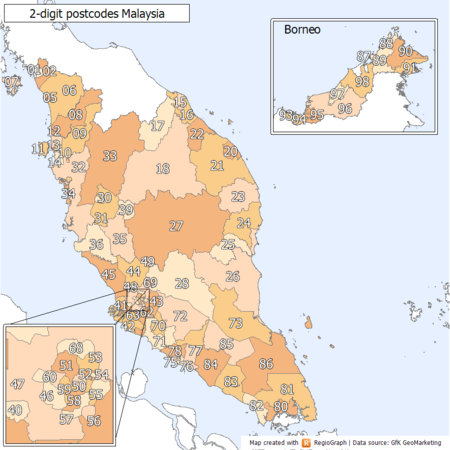
Postal codes in Malaysia, usually referred to as postcodes (Malay: poskod), are five digit numeric. The first two digits of the postcode denote the state or federal territory (e.g. 42000 Port Klang, Selangor). However, postcode area boundaries may cross state borders, as areas near to state borders may be served by post offices located in another state, and therefore use postcodes of the assigned post offices. History Malaysia's current postcode system was initiated by M. Rajasingam, director-ge…

FaceAlbum studio karya KeyDirilis26 November 2018 (2018-11-26)Direkam2018GenreK-popDurasi34:28BahasaKoreaLabel SM Entertainment iriver Kronologi Key Face(2018) Hologram(2018) Singel dalam album Face Forever YoursDirilis: 6 November 2018 One of Those NightsDirilis: 26 November 2018 Face adalah album debut dari penyanyi asal Korea Selatan, Key. Album ini dirilis pada tanggal 26 November 2018, melalui SM Entertainment. One of Those Nights dan Forever Yours (featuring Crush dan Soyou, masin…

PT Aero WisataKantor pusat Aerowisata di JakartaNama dagangAerowisataJenisPerseroan terbatasIndustriPariwisata dan logistikDidirikan30 Juni 1973; 50 tahun lalu (1973-06-30)KantorpusatJakarta, IndonesiaWilayah operasiIndonesiaTokohkunciBeni Gunawan[1](Direktur Utama)Irfan Setiaputra[1](Komisaris Utama)ProdukHotelMerekAerofood ACSPramaKilaAsanaAerotravelAeroMICEAerohajjGaruda Indonesia HolidaysAerotransAeroExpressGIA CharterJasaKateringPengaturan perjalananLogistikPenyewaan mo…

Supreme Court of the United States38°53′26″N 77°00′16″W / 38.89056°N 77.00444°W / 38.89056; -77.00444EstablishedMarch 4, 1789; 235 years ago (1789-03-04)LocationWashington, D.C.Coordinates38°53′26″N 77°00′16″W / 38.89056°N 77.00444°W / 38.89056; -77.00444Composition methodPresidential nomination with Senate confirmationAuthorized byConstitution of the United States, Art. III, § 1Judge term lengthlife …

Listes de films américains ◄◄ 1909 1910 1911 1912 1913 1914 1915 1916 1917 ►► Liste de films américains sortis en 1913. A-Z (Ordre alphabétique des titres en anglais) Titre Réalisateur Distribution Genre Notes The Adventures of Kathlyn Francis J. Grandon Kathlyn Williams Sérial aventure American Born Sydney Ayres, Harry von Meter, Charles Cummings Article 47, L' William Garwood, Victory Bateman, Howard Davies Atlantis Barney Oldfield's Race for a Life Mack Sennett Mack Sennett, Mabe…

Bupati Kabupaten Parigi MoutongLambang Parigi MoutongPetahanaRichard Arnaldo DjanggolaPenjabatsejak 12 Oktober 2023KediamanRumah Jabatan Bupati Parigi MoutongMasa jabatan5 tahunDibentuk2002Pejabat pertamaLongki DjanggolaSitus webparigimoutongkab.go.id Bupati Parigi Moutong (Inggris: Regent of Parigi Moutong), adalah seseorang yang memegang kekuasaan tertinggi dalam lingkup Pemerintahan Kabupaten Parigi Moutong di Parigi Moutong, Sulawesi Tengah, Indonesia. Pada dasarnya, Bupati Parigi M…

Italian architect Lyme Park, Cheshire designed by Giacomo Leoni. The original Tudor mansion was transformed by Leoni into an Italian palazzo. The design was altered by English architect Lewis Wyatt's 19th-century addition of the box-like structure surrounding the centre pediment. This squat tower is in place of Leoni's intended cupola. Giacomo Leoni (1686 – 8 June 1746), also known as James Leoni, was an Italian architect, born in Venice. He was a devotee of the work of Florentine Renaissance …

Football club (German: Fußballclub, FC) was a designation for a specially promoted club for elite football in East Germany. The football clubs were formed in 1965 and 1966 as centers of excellence in East German football. The football clubs enjoyed considerable advantages over other sports communities in East German football in terms of material conditions and talent recruitment. All designated football clubs had their own catchment areas and promising players were ordered to play for them. In …

Galaxy in the constellation Cetus NGC 560SDSS image of NGC 560Observation data (J2000 epoch)ConstellationCetusRight ascension01h 27m 25.434s[1]Declination−01° 54′ 46.54″[1]Redshift0.018289[2]Heliocentric radial velocity5433 km/s[2]Distance250.4 ± 17.6 Mly (76.78 ± 5.39 Mpc)[3]Apparent magnitude (B)14.0[2]CharacteristicsTypeS00[3]Other designationsUGC 1036, MCG +00-04-151, PGC…

Historic neighborhood in Massachusetts For other uses, see Beacon Hill (disambiguation). United States historic placeBeacon Hill Historic DistrictU.S. National Register of Historic PlacesU.S. National Historic Landmark District Park Street, looking toward the Massachusetts State HouseShow map of BostonShow map of MassachusettsShow map of the United StatesLocationBoston, MassachusettsBuilt1795ArchitectCharles BulfinchArchitectural styleColonial Revival, Greek Revival, FederalWebsitewww.beaco…

2006 studio album by Paul McCartneyEcce Cor MeumStudio album by Paul McCartneyReleased25 September 2006Recorded13–17 March 2006StudioAbbey Road, LondonGenreClassical, carol, hymnLength56:50LanguageEnglish, LatinLabelEMI ClassicsProducerJohn FraserPaul McCartney chronology Never Stop Doing What You Love(2005) Ecce Cor Meum(2006) Memory Almost Full(2007) Paul McCartney classical album chronology Working Classical(1999) Ecce Cor Meum(2006) Ocean's Kingdom(2011) Professional ratingsReview …

Голубянки Самец голубянки икар Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ПервичноротыеБез ранга:ЛиняющиеБез ранга:PanarthropodaТип:ЧленистоногиеПодтип:ТрахейнодышащиеНадкласс:ШестиногиеКласс:Н�…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2022) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: National Ne…

هنودمعلومات عامةنسبة التسمية الهند التعداد الكليالتعداد قرابة 1.21 مليار[1][2]تعداد الهند عام 2011ق. 1.32 مليار[3]تقديرات عام 2017ق. 30.8 مليون[4]مناطق الوجود المميزةبلد الأصل الهند البلد الهند الهند نيبال 4,000,000[5] الولايات المتحدة 3,982,398[6] الإمارا�…



