Species in reptile order Crocodilia
Three extant crocodilian species clockwise from top-left: saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus ), American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis ), and gharial (Gavialis gangeticus ) Crocodilia is an order of mostly large, predatory , semiaquatic reptiles , which includes true crocodiles , the alligators , and caimans ; as well as the gharial and false gharial . A member of this order is called a crocodilian, or colloquially a crocodile.
The 9 genera and 28 species of Crocodilia are split into 3 subfamilies: Alligatoridae , alligators and caimans; Crocodylidae , true crocodiles; and Gavialidae , the gharial and false gharial.
Conventions
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species . Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the crocodilian's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN red list for that species unless otherwise noted. All extinct species or subspecies listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "†". Population figures are rounded to the nearest hundred.
Classification
The order Crocodilia consists of 28 extant species belonging to 9 genera. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Modern molecular studies indicate that the 9 genera can be grouped into 3 families.
Crocodilians
Family Alligatoridae
The extant Alligatoridae can be recognised by the broad snout, in which the fourth tooth of the lower jaw cannot be seen when the mouth is closed.[ 1]
Genus Alligator Cuvier , 1807
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
American alligator
A. mississippiensis Daudin , 1801Southeastern United States
Size : up to 450 kg (990 lb)Habitat : Wetlands (inland), intertidal marine, and coastal marine[ 2] Diet : [ 2] LC [ 2]
Chinese alligator
A. sinensis Fauvel , 1879Eastern China
Size : up to 45 kg (99 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 3] Diet : [ 3] CR [ 3]
Genus Caiman Spix , 1825
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
Spectacled caiman
C. crocodilus Linnaeus , 1758Northern South America and Central America
Size : up to 45 kg (99 lb)Habitat : Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[ 4] Diet : [ 4] LC [ 4]
Broad-snouted caiman
C. latirostris Daudin , 1802Southeastern South America
Size : up to 50 kg (110 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands and intertidal marine[ 5] Diet : [ 5] LC [ 5]
Yacare caiman
C. yacare Daudin , 1802Central and southern South America
Size : up to 60 kg (130 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 6] Diet : [ 6] LC [ 6]
Genus Melanosuchus Gray , 1862
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
Black caiman
M. niger Spix , 1825Northern South America
Size : up to 500 kg (1,100 lb)Habitat : [ 7] Diet : [ 7] LC [ 7]
Genus Paleosuchus Gray , 1862
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
Cuvier's dwarf caiman
P. palpebrosus Cuvier , 1807Northern and central South America
Size : typically 6–7 kg (13–15 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 8] Diet : [ 8] LC [ 8]
Smooth-fronted caiman
P. trigonatus Schneider , 1801Northern South America
Size : typically 9–20 kg (20–44 lb)Habitat : Forest and inland wetlands[ 9] Diet : [ 9] LC [ 9]
Family Crocodylidae
The extant Crocodylidae have a variety of snout shapes, but can be recognised because the fourth tooth of the lower jaw is visible when the mouth is closed.[ 1]
Genus Crocodylus Laurenti , 1768
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
American crocodile
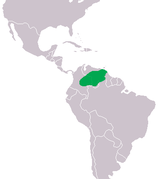
C. acutus Cuvier , 1807Northern South America, Central America, Greater Antilles
Size : up to 500 kg (1,100 lb)Habitat : Forest, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and coastal marine[ 10] Diet : [ 10] VU [ 10]
Hall's New Guinea crocodile
C. halli Murray , Russo , Zorrilla , McMahan , New Guinea
Size : up to 3.5 m (11 ft) for males and 2.7 m (8.9 ft) for femalesHabitat : Swamps, rivers, and lakesDiet :
LC
Orinoco crocodile
C. intermedius Graves, 1819
Northern South America
Size : up to 635 kg (1,400 lb)Habitat : Forest, savanna, and inland wetlands[ 11] Diet : [ 11] CR [ 11]
Freshwater crocodile
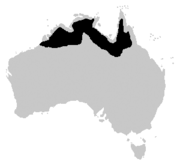
C. johnstoni Krefft , 1873Northern Australia
Size : up to 100 kg (220 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 12] Diet : [ 12] LC [ 12]
Philippine crocodile
C. mindorensis Schmidt , 1935Philippines Size : up to 90 kg (200 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 13] Diet : [ 13] CR [ 13]
Morelet's crocodile
C. moreletii Duméril , 1851Eastern Mexico
Size : up to 150 kg (330 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 14] Diet : [ 14] LC [ 14]
Nile crocodile
C. niloticus Laurenti , 1768Sub-Saharan Africa
Size : up to 750 kg (1,650 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and coastal marine[ 15] Diet : [ 15] LC [ 15]
New Guinea crocodile
C. novaeguineae Schmidt , 1928New Guinea Size : up to 200 kg (440 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 16] Diet : [ 16] LC [ 16]
Mugger crocodile
C. palustris Lesson , 1831Southern Asia
Size : up to 400 kg (880 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands and neritic marine[ 17] Diet : [ 17] VU [ 17]
Saltwater crocodile
C. porosus Schneider , 1801South and Southeast Asia, northern Australia and Oceania
Size : up to 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)Habitat : [ 18] Diet : [ 18] LC [ 18]
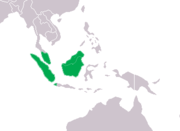
Borneo crocodile
C. raninus Müller , 1844Borneo
Size : Habitat : Diet :
NE
Cuban crocodile
C. rhombifer Cuvier , 1807Cuba Size : up to 215 kg (474 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 19] Diet : [ 19] CR [ 19]
Siamese crocodile
C. siamensis Schneider , 1801Southeast Asia
Size : up to 120 kg (260 lb)Habitat : Inland wetlands[ 20] Diet : [ 20] CR [ 20]
West African crocodile
C. suchus Geoffroy , 1807Western and central Africa
Size : Habitat : Diet :
NE
Family Gavialidae
Gavialidae can be recognised by the long narrow snout, with an enlarged boss at the tip.[ 1]
Genus Gavialis Oppel, 1811 – one species
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
Gharial
G. gangeticus Gmelin , 1789Scattered south Asia
Size : up to 680 kg (1,500 lb)Habitat : Wetlands (inland)[ 23] Diet : [ 23] CR [ 23]
Genus Tomistoma Müller , 1846
Common name
Scientific name and subspecies
Range
Size and ecology
IUCN status and estimated population
False gharial
T. schlegelii Müller , 1838Southeast Asia
Size : up to 270 kg (600 lb)Habitat : Forest and inland wetlands[ 24] Diet : [ 24] EN [ 24]
References
^ a b c Lang, J. W. (2002). "Crocodilians". In Halliday, T.; Adler, K. (eds.). The Firefly Encyclopedia of Reptiles and Amphibians 212–221 . ISBN 978-1-55297-613-5 ^ a b c Elsey, R.; Woodward, A.; Balaguera-Reina, S. A. (2019). "Alligator mississippiensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T46583A3009637. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T46583A3009637.en ^ a b c Jiang, H.; Wu, X. (2018). "Alligator sinensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T867A3146005. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T867A3146005.en ^ a b c Balaguera-Reina, S. A.; Velasco, A. (2019). "Caiman crocodilus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T46584A3009688. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T46584A3009688.en ^ a b c Siroski, P.; Bassetti, L. A. B.; Piña, C.; Larriera, A. (2020). "Caiman latirostris " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T46585A3009813. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T46585A3009813.en ^ a b c Campos, Z.; Llobet, A.; Magnusson, W. E.; Piña, C. (2020). "Caiman yacare " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020 : e.T46586A3009881. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T46586A3009881.en ^ a b c Ross, J. P. (2000). "Melanosuchus niger " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2000 : e.T13053A3407604. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2000.RLTS.T13053A3407604.en ^ a b c Magnusson, W. E.; Campos, Z.; Muniz, F. (2019). "Paleosuchus palpebrosus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T46587A3009946. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T46587A3009946.en ^ a b c Campos, Z.; Magnusson, W. E.; Muniz, F. (2019). "Paleosuchus trigonatus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T46588A3010035. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T46588A3010035.en ^ a b c Ponce-Campos, P.; Thorbjarnarson, J.; Velasco, A. (IUCN SSC Crocodile Specialist Group). (2012). "Crocodylus acutus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012 : e.T5659A3043244. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T5659A3043244.en ^ a b c Balaguera-Reina, S. A.; Espinosa-Blanco, A.; Antelo, R.; Morales-Betancourt, M.; Seijas, A. (2020) [errata version of 2018 assessment]. "Crocodylus intermedius " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018 : e.T5661A181089024. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T5661A181089024.en ^ a b c Isberg, S.; Balaguera-Reina, S. A.; Ross, J. P. (2017). "Crocodylus johnstoni " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017 : e.T46589A3010118. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T46589A3010118.en ^ a b c van Weerd, M.; C. Pomaro, C.; de Leon, J.; Antolin, R.; Mercado, V. (2016). "Crocodylus mindorensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016 : e.T5672A3048281. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T5672A3048281.en ^ a b c Cedeño-Vázquez, J. R.; Platt, S. G.; Thorbjarnarson, J. (IUCN Crocodile Specialist Group). (2012). "Crocodylus moreletii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012 : e.T5663A3045579. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T5663A3045579.en ^ a b c Isberg, S.; Combrink, X.; Lippai, C.; Balaguera-Reina, S. A. (2019). "Crocodylus niloticus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T45433088A3010181. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T45433088A3010181.en ^ a b c Solmu, G.; Manolis, C. (2019). "Crocodylus novaeguineae " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T46591A3010398. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T46591A3010398.en ^ a b c Choudhury, B. C.; de Silva, A. (2013). "Crocodylus palustris " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013 : e.T5667A3046723. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-2.RLTS.T5667A3046723.en ^ a b c Crocodile Specialist Group (1996). "Crocodylus porosus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 1996 : e.T5668A11503588. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T5668A11503588.en ^ a b c Targarona, R. R.; Soberón, R. R.; Cotayo, L.; Tabet, M. A.; Thorbjarnarson, J. (2017) [errata version of 2008 assessment]. "Crocodylus rhombifer " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008 : e.T5670A11516438. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T5670A11516438.en ^ a b c Bezuijen, M.; Simpson, B.; Behler, N.; Daltry, J.; Tempsiripong, Y. (2012). "Crocodylus siamensis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2012 : e.T5671A3048087. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2012.RLTS.T5671A3048087.en ^ a b c Shirley, M. H. (2014). "Mecistops cataphractus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014 : e.T5660A3044332. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-1.RLTS.T5660A3044332.en ^ a b c Crocodile Specialist Group (1996). "Osteolaemus tetraspis " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 1996 : e.T15635A4931429. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T15635A4931429.en ^ a b c Lang, J; Chowfin, S.; Ross, J. P. (2019) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Gavialis gangeticus " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019 : e.T8966A149227430. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T8966A149227430.en ^ a b c Bezuijen, M. R.; Shwedick, B.; Simpson, B. K.; Staniewicz, A.; Stuebing, R. (2014). "Tomistoma schlegelii " . IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014 : e.T21981A2780499. doi :10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-1.RLTS.T21981A2780499.en