María Parado de Bellido
|
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Steel guitar (disambigua). Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento strumenti musicali non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Steel guitarDiversi tipi di steel guitar: chitarra resofonica (a sinistra), lap steel (a destra)[1] e pedal st…

Ferenc Szálasi Pemimpin BangsaMasa jabatan16 Oktober 1944 – 28 Maret 1945Perdana MenteriDirinya sendiri PendahuluMiklós Horthy(wali)PenggantiDewan Nasional TinggiPerdana Menteri Hungaria ke-37Perdana Menteri Kerajaan Hungaria ke-13(de facto)Masa jabatan16 Oktober 1944 – 28 Maret 1945PemimpinDirinya sendiri PendahuluGéza LakatosPenggantiBéla Miklós(oposisi, kemudian secara resmi) Informasi pribadiLahir(1897-01-06)6 Januari 1897Kassa, County Abaúj-Torna, Kerajaan Hungar…

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Abdul Wahid Ash-Shalihi – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Syekh Abdul Wahid Ash-Shalihi (1878-1950), disebut pula Syekh Abdul Wahid Tabek Gadang atau gelarnya Baliau Tobek Godang, adalah s…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Bronisław DardzińskiLahir(1901-12-30)30 Desember 1901St. Petersburg, Kekaisaran Rusia (kini Rusia)Meninggal13 Mei 1971(1971-05-13) (umur 69)Warsawa, Republik Rakyat PolandiaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1938–1966 Bronisław Dardziński (30 Des…

سوزوبوليس تقسيم إداري البلد اليونان [1] خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 40°16′39″N 23°08′53″E / 40.27753889°N 23.148025°E / 40.27753889; 23.148025 الارتفاع 20 متر السكان التعداد السكاني 537 (إحصاء السكان) (2011) معلومات أخرى التوقيت ت ع م+02:00 (توقيت قياسي)، وت ع م+03:00 (توقيت صيفي) ال�…

Mike PosnerPosner tahun 2012LahirMichael Robert Henrion Posner[1]12 Februari 1988 (umur 36)Detroit, Michigan, Amerika SerikatPekerjaan Penyanyi penulis lagu produser rekaman rapper penyair Tahun aktif2008–sekarangKota asalSouthfield, Michigan, Amerika SerikatKarier musikGenre Pop hip hop R&B folk Instrumen Vokal gitar piano keyboard Label J RCA Island[2] Artis terkait Avicii Big Sean Situs webmikeposner.com Michael Robert Henrion Posner (/ˈpoʊznər/ POHZ-n�…

Species of lizard Not to be confused with Dunes sagebrush lizard. Sagebrush lizard Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Suborder: Iguania Family: Phrynosomatidae Genus: Sceloporus Species: S. graciosus Binomial name Sceloporus graciosusBaird & Girard, 1852[2] The sagebrush lizard or sagebrush swift (Sceloporus graciosus) is a common species of p…

Editora GloboIndustriPenerbitanGenreBerbagaiDidirikan1883PendiriL. P. de Barcellos & S. A. PintoKantorpusatPorto AlegreCabangBrasilWilayah operasi BrasilProdukBukuIndukGrupo GloboSitus webeditoraglobo.globo.com Editora Globo (Editor Globo) adalah sebuah penerbit Brasil dihormati, properti yang dimiliki oleh Fundação Roberto Marinho. Ini dimulai sebagai sebuah toko buku yang disebut Livraria do Globo, didirikan di Porto Alegre, pada bulan Desember 1883, oleh Laudelino Pinheiro de Barce…

Florian Hübner Florian Hübner pada Oktober 2013Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Florian HübnerTanggal lahir 1 Maret 1991 (umur 33)Tempat lahir JermanTinggi 191 m (626 ft 7+1⁄2 in)Posisi bermain Bek tengahInformasi klubKlub saat ini Borussia Dortmund IINomor 2Karier junior0000–2009 SV Wehen WiesbadenKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2009–2011 SV Wehen Wiesbaden II 23 (1)2009–2011 SV Wehen Wiesbaden 23 (0)2011– Borussia Dortmund II 17 (3)Tim nasional‡2010–20…
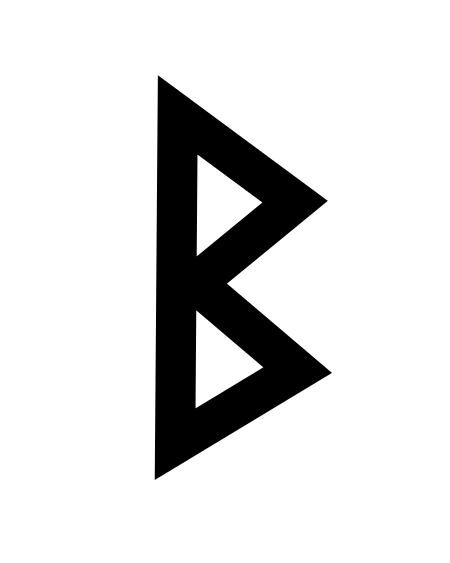
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發展…

Darla K. AndersonAnderson pada Oktober 2010LahirDarla Kay AndersonGlendale, California, ASTempat tinggalNoe Valley, San Francisco, California, AS[1]PekerjaanProduserTempat kerjaPixar Animation Studios (1993–2018)Suami/istriKori Rae (2004, 2008–sekarang)[1] Darla Kay Anderson adalah seorang produser film Amerika Serikat yang dulunya berkarya di Pixar Animation Studios.[2] Ia merupakan anggota badan direktur nasional untuk Producers Guild of America.[3] Referens…

British photographer Pete OxfordNationalityBritishCitizenshipBritishOccupationPhotographerWebsitehttp://peteoxford.com/ Pete Oxford is a British-born conservation photographer based in Cape Town, South Africa, after living in Quito, Ecuador for several years. Originally trained as a marine biologist, he and his wife, South African-born Reneé Bish, now work as a professional photographic team focusing primarily on wildlife and indigenous cultures. Oxford is a founding fellow of the International…

Nigerian Highlife band The Cavemen.Background informationOriginImo State, NigeriaGenresHighlifeInstrument(s)Bass, drumsYears active2020–presentLabelsSounds From The CaveMembersKingsley Okorie Benjamin James The Cavemen (stylized as The Cavemen.) are a Nigerian highlife band consisting of sibling duo Kingsley Okorie, a bassist, and Benjamin James, a drummer. They were discovered by Lady Donli and are known for their live performances.[1] They won the 2020 Headies Award for the Best Alte…

Chinese kingdom (220–266) during the Three Kingdoms period This article is about the Three Kingdoms state. For the Northern and Southern Dynasties Wei dynasty, see Northern Wei. For the modern curator, see Cao Wei (curator). Former Wei redirects here. For other no longer extant Weis, see Wei (disambiguation). Wei魏220–266The territories of Cao Wei (in yellow), 262 AD.CapitalXuchang (220–226),[1] Luoyang (226–266)Common languagesMiddle ChineseReligion Taoism, Confucianism, C…

Il governo Monti, gabinetto tecnico formato nel novembre 2011 a seguito della crisi del governo Berlusconi IV e degli effetti della congiuntura economica. Un governo tecnico, o anche governo dei tecnici,[1] è un tipo di governo dalla non dichiarata identità politica,[2][3] formato da personalità dotate di competenze tecniche specialistiche ed estranee alle forze politiche;[4] tale tipo di governo viene solitamente costituito in particolari situazioni in cui coe…

VerzycomuneVerzy – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Francia RegioneGrand Est Dipartimento Marna ArrondissementReims CantoneMourmelon-Vesle et Monts de Champagne TerritorioCoordinate49°09′N 4°10′E / 49.15°N 4.166667°E49.15; 4.166667 (Verzy)Coordinate: 49°09′N 4°10′E / 49.15°N 4.166667°E49.15; 4.166667 (Verzy) Superficie13,43 km² Abitanti1 078[1] (2009) Densità80,27 ab./km² Altre informazioniCod. postale51380 Fuso orari…

Ne doit pas être confondu avec Vieux-Port de Marseille. Grand port maritime de MarseilleTerminaux passagers du bassin Est (Marseille).PrésentationOpérateur Établissement public du Grand port maritime de Marseille (d)Type Port de commerceStatut Grand port maritime (2008)Tirant d'eau 10-12 mTonnage 78,52 Mt (2014)[1]Trafic 2,46 M millions de passagers (dont 1,3 M de croisiéristes)[2],[3]1 179 910 conteneurs (2014)[1]Activités Tourisme, logistique, transport fluvial, conteneurs…

森川智之配音演员本名同上原文名森川 智之(もりかわ としゆき)罗马拼音Morikawa Toshiyuki昵称モリモリ[1]、帝王[1]国籍 日本出生 (1967-01-26) 1967年1月26日(57歲) 日本東京都品川區[1](神奈川縣川崎市[2]、橫濱市[3]成長)职业配音員、旁白、歌手、藝人音乐类型J-POP出道作品外國人取向的日語教材代表作品但丁(Devil May Cry)D-boy(宇宙騎士�…

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) 土�…

American baseball player Baseball player Ryan DoumitDoumit with the Atlanta BravesCatcherBorn: (1981-04-03) April 3, 1981 (age 43)Moses Lake, Washington, U.S.Batted: SwitchThrew: RightMLB debutJune 5, 2005, for the Pittsburgh PiratesLast MLB appearanceSeptember 28, 2014, for the Atlanta BravesMLB statisticsBatting average.264Home runs104Runs batted in413 Teams Pittsburgh Pirates (2005–2011) Minnesota Twins (2012–2013) Atlanta Braves (2014) Ryan Matthew Doum…

