Major face vein
Blood vessel
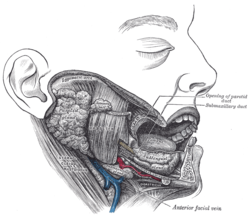
The retromandibular vein (temporomaxillary vein , posterior facial vein ) is a major vein of the face. It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein , and superficial temporal vein . It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein , while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein .
Anatomy
Origin
The retromandibular vein is formed within the parotid gland [ 1] maxillary vein , and superficial temporal vein .[ 1] [ 2] [ 3]
Course
It descends inside parotid gland ,[ 1] [ 4] external carotid artery (but beneath the facial nerve ),[ 4] sternocleidomastoideus muscle and ramus of mandible .[citation needed It emerges from the parotid gland inferiorly, then immediately divides into two branches:[ 1]
Function
The retromandibular vein provides venous drainage to the superior cranium , and significant drainage to the ear .[ 7]
Clinical significance
Parrot's sign is a sensation of pain when pressure is applied to the retromandibular region.[citation needed
Additional images
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 646 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
^ a b c d e Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 364. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0 ^ Thompson, Stevan H.; Yeung, Alison Y. (2016-01-01), Hupp, James R.; Ferneini, Elie M. (eds.), "4 - Anatomy Relevant to Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections" , Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections , St. Louis: Elsevier, pp. 60– 93, doi :10.1016/b978-0-323-28945-0.00004-1 , ISBN 978-0-323-28945-0 , retrieved 2020-11-11 ^ Cunningham, Larry L.; Card, Aaron Sterling (2012-01-01), Bagheri, Shahrokh C.; Bell, R. Bryan; Khan, Husain Ali (eds.), "Chapter 38 - Mandibular Subcondylar Fractures" , Current Therapy In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery , Saint Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 298– 304, doi :10.1016/b978-1-4160-2527-6.00038-4 , ISBN 978-1-4160-2527-6 , retrieved 2020-11-11 ^ a b Loukota, Richard A.; Abdel-Galil, Khalid (2017-01-01), Brennan, Peter A.; Schliephake, Henning; Ghali, G. E.; Cascarini, Luke (eds.), "6 - Condylar Fractures" , Maxillofacial Surgery (Third Edition) , Churchill Livingstone, pp. 74– 92, doi :10.1016/b978-0-7020-6056-4.00006-x , ISBN 978-0-7020-6056-4 , retrieved 2020-11-11 ^ a b Cramer, Gregory D. (2014-01-01), Cramer, Gregory D.; Darby, Susan A. (eds.), "Chapter 5 - The Cervical Region" , Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and Ans (Third Edition) , Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 135– 209, doi :10.1016/b978-0-323-07954-9.00005-0 , ISBN 978-0-323-07954-9 , retrieved 2020-11-11 ^ Drake, Richard L. (Richard Lee), 1950- (2005). Gray's anatomy for students ISBN 0-443-06612-4 OCLC 55139039 . {{cite book }}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link ) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link )^ Posnick, Jeffrey C. (2014-01-01), Posnick, Jeffrey C. (ed.), "39 - Aesthetic Alteration of Prominent Ears: Evaluation and Surgery" , Orthognathic Surgery , St. Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 1703– 1745, doi :10.1016/b978-1-4557-2698-1.00039-3 , ISBN 978-1-4557-2698-1 , retrieved 2020-11-11
External links