|
Interspinous ligament
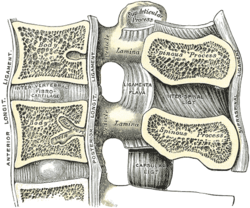
The interspinous ligaments (interspinal ligaments) are thin, membranous ligaments that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine.[1][2] They take the form of relatively weak sheets of fibrous tissue and are well developed only in the lumbar region.[3] They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process. They meet the ligamenta flava anteriorly,[4][better source needed] and blend with the supraspinous ligament[3] posteriorly at the apexes of the spinal processes. The function of the interspinous ligaments is to limit ventral flexion of the spine and sliding movement of the vertebrae.[5] The ligaments are narrow and elongated in the thoracic region. They are broader, thicker, and quadrilateral in form in the lumbar region. They are only slightly developed in the neck;[1] in the neck, they are often considered part of the nuchal ligament.[4][better source needed] References
External links
Information related to Interspinous ligament |
||||||||||||||||||||||