|
Local government in SabahThe local government in Sabah is the lowest level government in Sabah, Malaysia. It ranks third in the Malaysian government system after federal and state government. Local governments have the power to levy property taxes, to enact local laws and regulations, and to issue licenses and permits for any type of trade in their area. However, it also has the obligation to provide basic utilities, such as to regulate rubbish collection and waste disposal and to ensure urban or regional planning. The district and municipal constitution in Sabah is based on the Local Government Ordinance 1961. This ordinance also regulates the responsibilities and functions of community organs. A state ministry, the Ministry of Local Government and Housing, which was first established after the 1963 state elections, regulates the activities of the district/municipal authorities in the state of Sabah. Foundation of local administrationSabah is divided into administrative districts. The administrative districts are made up of towns and defined areas. These administrative districts, commonly referred to as the L.A.A (local authority area), will be governed by (depending on the status of the administrative district governed):
The basis of this structure is the Local Government Ordinance 1961. This decree empowers the Yang di-Pertua Negeri, among other things, to equip the districts with certain powers and to determine the names and boundaries of the districts. The structure of the administrative districts was first established in 1961 by this ordinance and then amended as necessary by decree (Administrative Divisions Proclamation).
Division to districts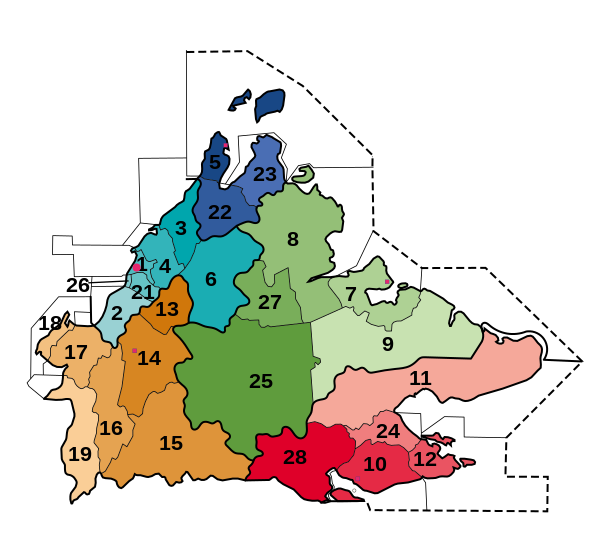
Sabah is initially divided into five administrative areas - Interior Division, Kudat Division, Sandakan Division, Tawau Division and West Coast Division. These administrative areas are assigned to districts. The administration of a district is the responsibility of a district officer. Associated with the district office is an assistant district officer. The administrative headquarters of the district is the District Office (Pejabat Daerah). Usually, the districts are named after the largest city/towns within the area or after the seat of the administration; For example, the town of Sandakan is the largest in the district of Sandakan under the Sandakan Division. Districts can be further subdivided into sub-districts (daerah kecil, literally "small district"). These do not represent a separate administrative level, but are to be understood as an "extended arm" of the district office, which perform certain administrative tasks in the district/municipalities. The status of a sub-district is an important step in the direction to achieve full district status. Until 2011, there were 11 sub-districts in Sabah:[25]
Status of administrative districtsSabah has three different types of administrative districts. The lowest level of a local authority is the district administered by a district council. There are certain criteria for upgrading:
The "Local Government Department of States of Malaysia" criteria for the status of a local authority comprise a number of requirements.[26] For example, Kota Kinabalu had to prove for his status as a city hall, among other things:
OthersDifferences from other statesUnlike other states in Malaysia, the administrative level of mukim does not exist in Sabah. In the context of the district/municipal administration in Sabah, mukim are a summary of various settlements and villages, which, however, are subordinate to the district offices. DependenciesIn contrast to the situation in Germany, where the municipal councils always represent the representation of the municipal citizens even in their different forms (municipal representation), the members of the "City Hall", the "Municipal Council" and the "District Council" are not democratically elected by the people as they are appointed by the Minister of Local Government and Housing. The effectiveness of local laws and regulations is also only established by their ratification by the Minister of State. Common abbreviationsWithin the administrative of Sabah, the following abbreviations are often found:[27]
See alsoNotes
References
External links |