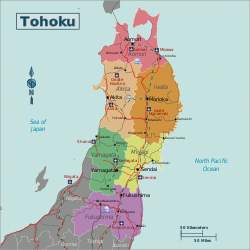
Tōhoku region
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Sonic Advance 2[a] adalah gim video platform gulir samping tahun 2002 dikembangkan oleh Dimps untuk Game Boy Advance.Ini adalah angsuran dalam seri Sonic the Hedgehog dan sekuel Sonic Advance 2001.Ceritanya mengikuti Sonic saat ia berangkat untuk menyelematkan teman-temannya dan mengambil Chaos Emeralds tujuh ajaib dari antagonis seri Doctor Eggman. Gameplay terdiri dari pemain yang menyelesaikan berbagai berbagai level sebagai salah satu dari lima karakter, masing-masing dengan atribut …

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2018年3月17日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:羅生門 (電影) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 此�…

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (مارس 2016) ملعب ألفريدو بيرانجيرمعلومات عامةسمّي باسم Alfredo Beranger (en) المنطقة الإدارية Lomas de Zamora Partido (en) البلد الأرجنتي�…

العلاقات الإماراتية الطاجيكستانية الإمارات العربية المتحدة طاجيكستان الإمارات العربية المتحدة طاجيكستان تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإماراتية الطاجيكستانية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الإمارات العربية المتحدة وطاجيكستان.[1][2][3][4&…

Public school division serving Loudoun County, Virginia, United States This section needs to be updated. The reason given is: Section needs to be updated for 2023-24 School Year.. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (November 2023) Loudoun County Public Schools (LCPS) is a branch of the Loudoun County, Virginia, United States government, and administers public schools in the county. LCPS's headquarters is located at 21000 Education Court in As…

Saint-François-Xavier, Paris Saint-François-Xavier, Paris adalah gereja Katolik Roma paroki di arondisemen ke-7 Paris yang didedikasikan untuk Fransiskus Xaverius, santo pelindung misi. Dibangun pada akhir abad ke-19, Itu memberi namanya ke stasiun Metro terdekat Saint-François-Xavier. Ini berisi makam Madeleine Sophie Barat, seorang santo Prancis dari Gereja Katolik dan pendiri Society of the Sacred Heart, sebuah lembaga pendidikan keagamaan di seluruh dunia. Ia juga dikenal dengan koleksi l…

Cumi asin Cumi asin adalah cumi-cumi yang diawetkan dengan garam kering dan kemudian disajikan untuk disantap. Pengeringan atau penggaraman, entah dengan garam kering atau air garam banyak dipakai sebagai metode pengawetan makanan laut.[1] Cumi asin umum ditemukan di negara-negara pantai Asia, khususnya Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, Hong Kong, Tiongkok Selatan, Korea Selatan dan Jepang. Di Indonesia, cumi asin biasa diolah menjadi aneka ragam hidangan, seperti sambal cumi, osen…

Santpoort NoordGeneral informationLocationNetherlandsCoordinates52°26′34″N 4°38′21″E / 52.44278°N 4.63917°E / 52.44278; 4.63917Line(s)Haarlem–Uitgeest railwayServices Preceding station Nederlandse Spoorwegen Following station Driehuistowards Hoorn NS Sprinter 4800 Santpoort Zuidtowards Amsterdam Centraal LocationSantpoort NoordLocation within Northern RandstadShow map of Northern RandstadSantpoort NoordSantpoort Noord (Netherlands)Show map of Netherlands San…

Gaurotes Gaurotes virginea Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Insecta Ordo: Coleoptera Famili: Cerambycidae Genus: Gaurotes Gaurotes adalah genus kumbang tanduk panjang yang tergolong famili Cerambycidae. Genus ini juga merupakan bagian dari ordo Coleoptera, kelas Insecta, filum Arthropoda, dan kingdom Animalia. Larva kumbang dalam genus ini biasanya mengebor ke dalam kayu dan dapat menyebabkan kerusakan pada batang kayu hidup atau kayu yang telah ditebang. Referensi …

Pasquale Fornara Nazionalità Italia Ciclismo Specialità Strada Termine carriera 1961 - ciclista Carriera Squadre di club 1946-1947S.C. Crennese1948Individuale1949-1951 Legnano1951-1953 Cilo1952 Bianchi1952-1954 Bottecchia1955 Bottecchia1955Leo-Chlorodont1956 Saint-Raphaël1956 Allegro1956-1957 Arbos1956-1958 Cilo1958 Ignis1959-1960 Emi1960 Mondia1961 Vov Nazionale 1953-1956 Italia Carriera da allenatore 1965 Cynar Stat…

ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Раннее христианство Гностическое христианство Вселенские соборы Ни�…

Chinese snack Kway japAlternative namesKuay jap, kueh japPlace of originSouthern ChinaMain ingredients rice sheets dark soy sauce pork offal braised meats hardboiled egg Similar dishesSekba, Burmese pork offal skewers Media: Kway jap Kway jap (Chinese: 粿汁; pinyin: guǒzhī; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: kóe-chiap), also spelt kuay jap is a Teochew noodle soup originating in Chinese cuisine consisting of flat, broad rice sheets (kway) in a soup made with dark soy sauce, served with an…

Teks Yunani dari risalah apologetik Origenes Contra Celsum, yang dianggap merupakan karya paling penting dari apologetik gereja perdana[1][2] Melawan Kelsos (Yunani: Κατὰ Κέλσου Kata Kelsou; Latin: Contra Celsum), yang sepenuhnya disajikan dalam bahasa Yunani, adalah sebuah karya apologetik besar karya bapa gereja Origenes dari Aleksandria. Karya tersebut ditulis pada sekitar tahun 248 dalam rangka melawan tulisan-tulisan Kelsos, seorang fisuf pagan dan kontroversialis…

For the Kyle song, see Light of Mine. For the Natasha Bedingfield song, see I Wanna Have Your Babies. 1992 single by PulpBabiesSingle by Pulpfrom the album His 'n' Hers Released5 October 1992Recorded20–24 July 1992StudioIsland Records Fallout Shelter, LondonGenre Britpop new wave LabelGift RecordsComposer(s)PulpLyricist(s)Jarvis CockerProducer(s)Ed BullerPulp singles chronology O.U. (Gone, Gone) (1992) Babies (1992) Razzmatazz (1993) Babies is a song written and released by British rock group …

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

Part of a series onRenewable energy Biofuel Biogas Biomass Carbon-neutral fuel Geothermal energy Geothermal heating Geothermal power Hydroelectricity Hydropower Marine current power Marine energy Osmotic power Solar energy Solar power Sustainable biofuel Tidal power Wave power Wind power Nuclear power proposed as renewable energy Topics by country and territory Marketing and policy trends vte The Pelamis Wave Energy Converter was a technology that used the motion of ocean surface waves to create…

Radko DimitrievFoto raffigurante Radko Dimitriev.NascitaGradec, 24 settembre 1859 MortePjatigorsk, 18 ottobre 1918 Cause della morteFucilato Dati militariPaese servito Bulgaria Impero russo Forza armata Esercito bulgaro Esercito imperiale russo Anni di servizio1877-1917 GradoTenente generale GuerreGuerra russo-turcaGuerra serbo-bulgaraPrima guerra balcanicaSeconda guerra balcanicaPrima guerra mondiale Comandante di3ª armata bulgara Studi militariScuola Militare di SofiaAccadem…

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6] 得…

Sierra de Cebollera Categoría UICN VI (área protegidade recursos gestionados) Pico Urbión desde la cima Castillo de VinuesaSituaciónPaís España EspañaComunidad La Rioja La RiojaMunicipios 2Lumbreras de CamerosVilloslada de Cameros Coordenadas 42°07′11″N 2°40′11″O / 42.11972222, -2.66972222Datos generalesAdministración Gobierno de La RiojaGrado de protección Parque naturalFecha de creación 1995Superficie 23 640 ha Sierra …

Sports radio station in Toronto This article is about CHUM, the Toronto radio station branded TSN Radio 1050 since April 13, 2011. For the national radio network, see TSN Radio. For the defunct broadcasting company that operated from 1945 to 2007, see CHUM Limited. For the radio network branded as CHUM, see CHUM-FM. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.F…